Measurement Uncertainty (MU) in Chemical Pathology
If you would like more information on measurement uncertainty, or you have any queries about any of the values generated below, then please contact the Duty Biochemist on 0300 422 5238.
What is measurement uncertainty?
With every result produced by a laboratory there is an associated uncertainty, which may be attributed to a number of small variations arising at any stage of the analytical process, from sample collection to analysis. It is important to understand that uncertainty is not the same as an error. An error implies that there is a difference between a measured value and the true value caused by an unknown factor, whereas uncertainty is an acceptable interval within which a result can fall. We are able to predict this interval by calculating the measurement uncertainty (MU) for each analyte in our repertoire.
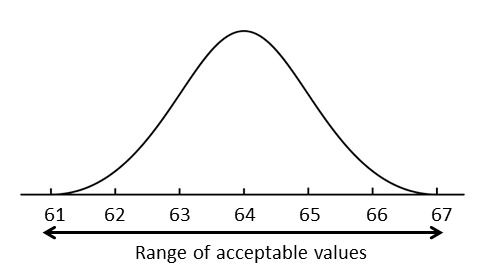
For example, if a “serum rhubarb” result of 64 µmol/L is reported by the laboratory, the result could actually lie somewhere between 61 and 67 µmol/L once MU is considered (figure 1).
Why are we reporting uncertainty?
By estimating and reporting uncertainty, the laboratory can indicate the quality and reliability of the result produced.
This information can then be used by clinicians and service users to compare a result to a cut-off limit or to a previous result from a sample on that same patient. Such information can be used by a clinician to determine whether the difference between two results is negligible due to uncertainty or significant due to a change in the condition of the patient. Without an estimate of MU, results cannot be compared either to previous results or reference values.
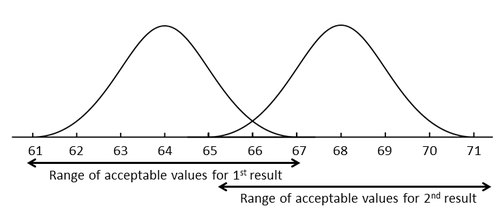
When there is a small change in the results, for example a change in serum rhubarb from 64 to 68 µmol/L, the range of acceptable values surrounding the two results may overlap (see figure below). The closer these results lie together the less likely they are to be significant but by knowing the MU we can be more confident in our ability to interpret the results.
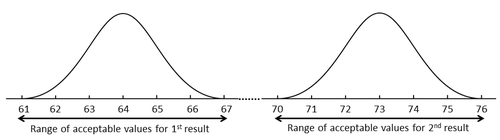
Where there is no overlap, for example a change in serum rhubarb from 64 to 73 µmol/L, we can be certain that a true change has occurred (see figure below).
The patient can then either be monitored or treated depending on any clinical cut-off limits that surround this result.
Measurement uncertainty values for analytes we assay
The table below shows the MU for each analyte currently assayed across the two laboratory sites.
| Analyte | MU (%) |
|---|---|
| Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) | 4.1 |
| Albumin | 2.4 |
| Alpha Foetoprotein (AFP) | 3.1 |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) | 1.9 |
| Ammonia | 16.8 |
| Amylase | 1.5 |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) | 3.2 |
| Beta Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin (bHCG) | 3.4 |
| Bicarbonate | 4.4 |
| Bile Acids | 4.1 |
| Bilirubin: Total | 4.3 |
| Bilirubin: Conjugated | 3.2 |
| CA125 | 2.9 |
| CA153 | 8.5 |
| CA199 | 5.7 |
| C-Reactive Protein (CRP) | 4.9 |
| Calcium | 1.8 |
| Carbamazepine | 2.8 |
| Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) | 3.6 |
| Chloride | 0.8 |
| Cholesterol | 1.8 |
| Cortisol | 3.0 |
| Creatine Kinase (CK) | 1.9 |
| Creatinine | 2.1 |
| Digoxin | 5.0 |
| Ethanol (Alcohol) | 3.3 |
| Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) | 3.4 |
| Free T3 (FT3) | 3.5 |
| Free T4 (FT4) | 3.0 |
| Gamma Glutamyltransferase (GGT) | 1.6 |
| Gentamicin | 6.0 |
| Glucose | 1.3 |
| Growth Hormone | 2.5 |
| HbA1c | 4.1 |
| High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) | 2.1 |
| Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF-1) | 3.7 |
| Iron | 1.7 |
| Lactate | 2.2 |
| Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) | 1.8 |
| Lithium | 3.2 |
| Luteinising Hormone (LH) | 3.3 |
| Macroprolactin | 3.8 |
| Magnesium | 2.3 |
|
N-terminal Pro-brain Natriuretic Peptide (NT-proBNP) |
2.9 |
| Oestradiol | 4.1 |
| Osmolality | 0.7 |
| Paracetamol | 5.2 |
| Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) | 3.7 |
| Phenytoin | 3.1 |
| Phosphate | 2.3 |
| Procalcitonin | 4.2 |
| Placental Growth Factor (PlGF) | 4.2 |
| Progesterone | 3.8 |
| Prolactin | 3.7 |
| Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) | 3.8 |
| Potassium | 1.4 |
| Salicylate | 2.4 |
| Sex Hormone Binding Globulin (SHBG) | 2.2 |
| Sodium | 0.8 |
| Soluable fms-like Tyrosine Kinase-1 (sFlt-1) | 4.4 |
| Tacrolimus | 6.4 |
| Testosterone | 5.2 |
| Theophylline | 3.5 |
| Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) | 3.6 |
| Thyroglobulin | 3.9 |
| Thyroglobulin Antibodies | 4.5 |
| Tobramycin | 3.4 |
| Total Protein | 2.0 |
| Transferrin | 3.1 |
| Triglyceride | 1.8 |
| Troponin T | 6.2 |
| Urate | 1.5 |
| Urea | 3.7 |
| Vancomycin | 4.2 |
| Vitamin D | 7.2 |
| Analyte | MU (%) |
|---|---|
| Amylase | 0.9 |
| Calcium | 1.8 |
| Creatinine | 2.2 |
| Magnesium | 2.6 |
| Microalbumin | 2.3 |
| Osmolality (urine) | 0.5 |
| Phosphate | 2.3 |
| Potassium | 1.9 |
| Protein | 7.8 |
| Sodium | 1.5 |
| Urate | 2.3 |
| Urea | 3.8 |
| Analyte | MU (%) |
|---|---|
| Faecal Calprotectin | 28.3 |
| Analyte | MU (%) |
|---|---|
| CSF Bilirubin (Xanthochromia) | 6.0 |
| CSF Haemoglobin (Xanthochromia) | 6.8 |
| CSF Glucose | 1.5 |
| CSF Lactate | 1.8 |
| CSF Protein | 2.8 |
| Analyte | MU (%) |
|---|---|
| Sweat Chloride | 2.9 |
Last updated: 14/01/2025