Lead (Pb)
Chemical Pathology
Notes
Lead poisoning can occur as a result of environmental exposure and this can cause permanent health damage, especially among children. The main sources of lead exposure in the UK are air-borne lead (from industrial sources), water-borne lead (where lead dissolves readily from lead piping or from lead solder in water pipes, sometimes found in pre-1970s buildings), and occupational and hobby exposure (e.g. plumbers and stained glass artists).
Lead poisoning can affect many parts of the body, including the central nervous system, kidneys, and reproductive organs. Symptoms include abdominal pain, fatigue, weakness, (aplastic) anaemia, basophilic stippling of erythrocytes and peripheral neuropathy.
In children especially, lead impairs cognitive development, which can lead to learning disabilities and behavioural problems. At very high levels, it can even result in hallucinations, coma, seizures, and death.
Indications for testing:
- Clinical signs and symptoms where lead exposure is suspected e.g. children with pica
- Occupational exposure, e.g. plumbers, lead miners, shipbuilders, construction workers, demolition workers and pottery manufacturers should be screened for lead exposure
- Adults with hobbies that involve lead-based paints, ceramics, soldering etc should also be tested.
Sample requirements
For adults, 4 ml of blood taken into an EDTA tube
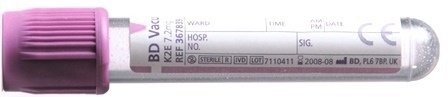
For children, blood taken into a 2mL EDTA tube
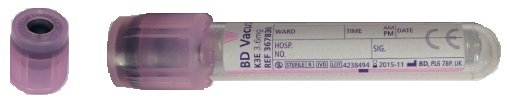
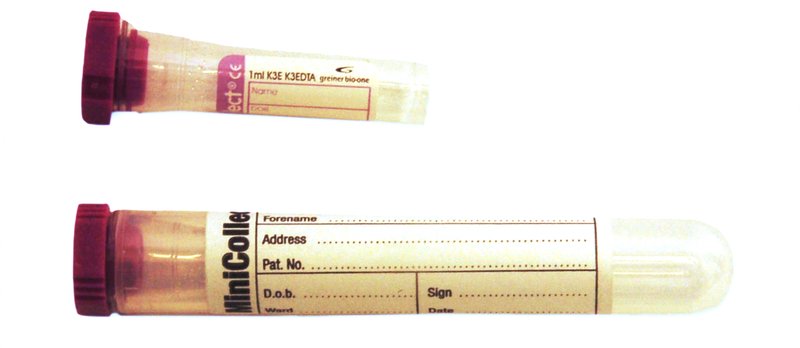
For infants, blood taken into a 1mL minicollect EDTA tube
Storage/transport
Send at ambient temperature to the laboratory. If unavoidable, samples can be stored refrigerated overnight.
Required information
Relevant clinical details including details of possible exposure and clinical signs and symptoms. If for occupational screening purposes, please include billing address.
Turnaround times
Samples are sent to a referral laboratory for analysis with results expected back within 2 weeks.
Reference ranges
Reference ranges are supplied by the assaying laboratory with the result reports.
Unit conversion:
- µmol/L x 20.7 = µg/dL
- µg/dL x 0.05 = µmol/L
Further information
To learn more about lead visit Lab Tests Online
For healthcare professionals, access TOXBASE
Page last updated: 07/02/2019