Streptococcal antibodies (aso)
Microbiology
Notes
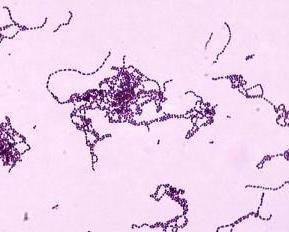
- This investigation comprises anti-streptolysin O antibodies (ASO).
- Guidance on interpretation can be found at the Public Health England website.
ASO antibodies
- Streptolysin O is produced by almost all strains of S.pyogenes (group A streptococci) and many group C and group G beta haemolytic streptococci
- May be used for diagnosis of recent streptococcal infections such as pharyngitis and tonsillitis but is unable to distinguish between infections with groups A, C and G streptococci. At best 80% of cases have positive ASO serology. The preferred method for acute sore throat is a bacterial throat swab for culture and sensitivity.
- Useful for acute rheumatic fever, 80% positivity
- Not very useful for infections such as impetigo and pyoderma
- False positives may occur in jaundiced patients with liver disease
- ASO rises 1 week after infection and peaks within 3-5 weeks returning to normal after 6-12 months
Sample requirements
Serum - paired samples not normally required
8.5ml of blood taken into a plain gel tube
Required information
- Relevant clinical details
- Date of onset
Storage/transport
Store at fridge temperature
Transport as soon as possible at ambient temperature
Turnaround time
Up to 8 days